
It is important to ensure traceability throughout the lifecycle of the project. See diagram below for some of the main reasons for this.
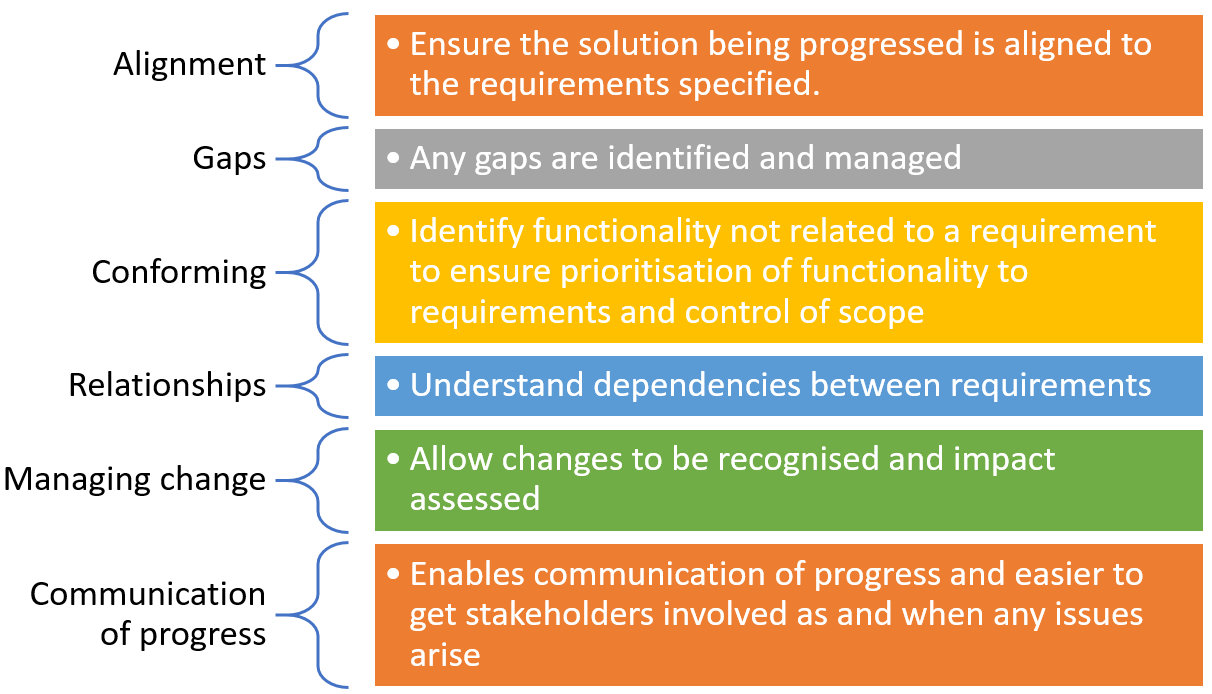
Traceability has several lenses that occur throughout the project lifecycle.
Here is a list of some of lenses to be considered for ensuring traceability:
- Business Requirements trace back to the scope, objectives, problem statement and needs.
- Solution requirements trace back to the business requirements
- Development traces back to the solution requirements
- Testing traces back to the solution and business requirements
The business analyst is normally the best placed team member to carry out these assessments because they understand the requirements, the detail behind them, the success criteria and have regular contact with all of the key team players.
To enable this the following activities are required:
- The business analyst can check themselves when gathering the Business Requirements that they trace back to the scope, objectives, problem statement and needs. If it doesn’t then the following is to be ascertained:
- Does the scope need to change? If so the impact of this needs to be assessed and managed.
- Is the requirement necessary? Requirements could be specified that when validated could be gold plating, only stated because has always been done a certain way or could belong to another project or phase. This exercise makes sure the requirements are challenged to ensure the right priority; the requirements can be measured against the objectives and overcome the problems identified.
- The business analyst to be a key reviewer or signatory to each of the other phases. They should have regular contact with all of the team members involved and should have time set aside to review each of the deliverables produced and regular check point meetings.
- A method needs to be established for reporting back on progress, dependencies and possible impacts that aren’t overly cumbersome but add value. This could involve charts and graphs to show progress and highlight gaps outstanding and difficulties.
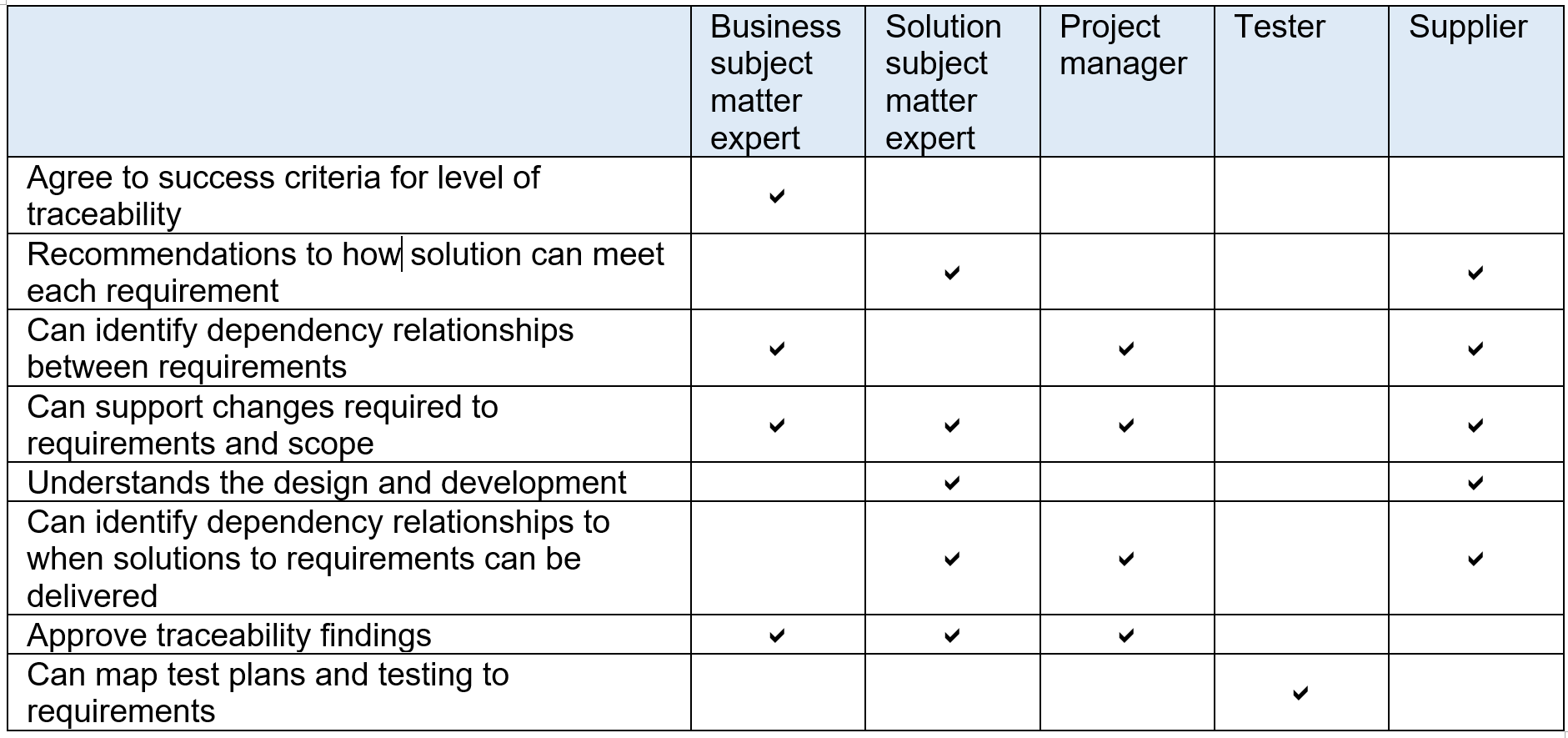
See matrix below for the types of stakeholders the Business Analyst will need to consult when conducting traceability and the reasons why.
Thoughts? Questions? Please share in the comments.

